California Earthquake Authority CEA
- CATRisk Consultants

- 5 nov 2020
- 6 Min. de lectura
Actualizado: 9 nov 2020
17th January 1994 Northridge earthquake cost the state of California 15.3 bn $ (26.4 bn $ in 2018 money terms). The insurance industry ended up paying in earthquake premium more than it had collected in the previous 30 years. So, to avoid bankruptcy or rather insolvency, most insurers began to limit, by writing fewer new homeowners’ policies. Most insurers filed for both rate increases and deductible increases from the original 10% to 15% or higher. This triggered a crisis by mid-1996 threatened the vitality of the state’s housing market and stalled state’s recovery from recession.
In 1996, California legislature established the CEA, California Earthquake Authority, as a publicly managed largely privately funded entity operating only in California.
CEA is the largest provider of residential earthquake insurance in the United States.
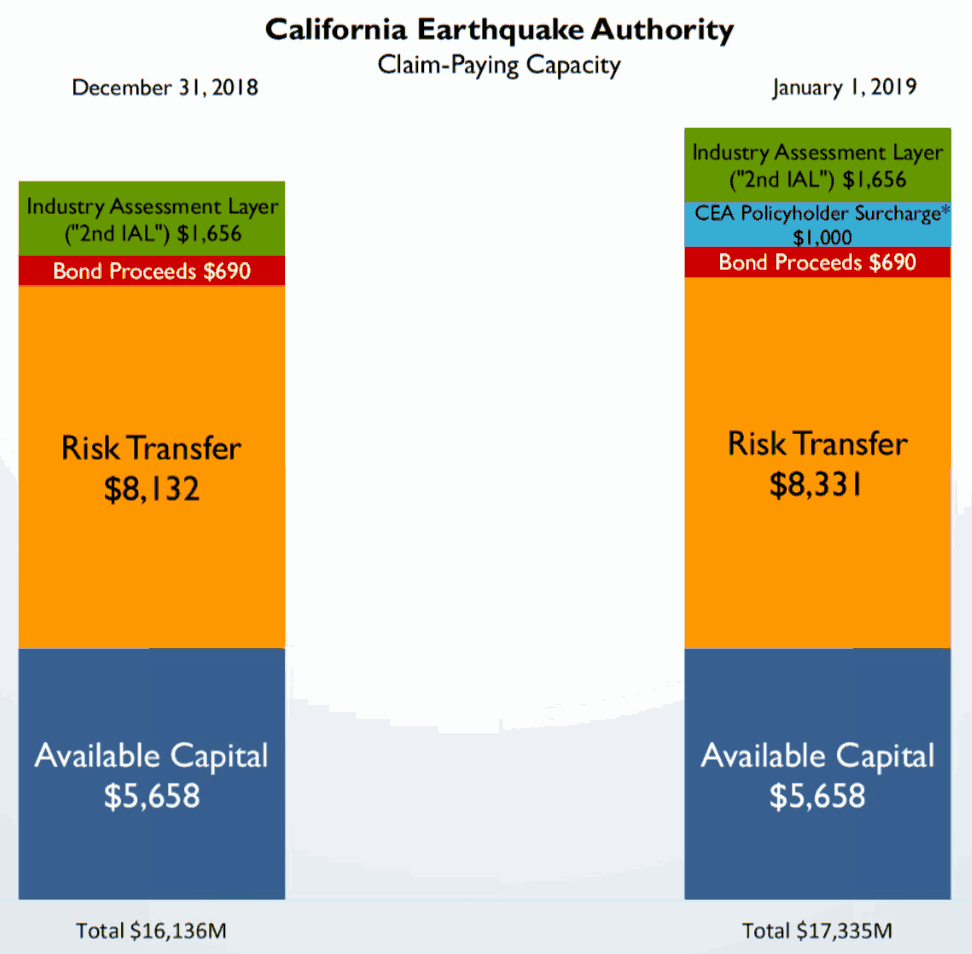
In 2005 it had underwritten circa 756,000 homeowners’ policies, corresponding to a total of 150 bn$ of aggregate exposure. In 2020 there are over 1.1 million policies with an estimated 522 bn$ of aggregate exposure. To protect this exposure CEA buys a catastrophe excess of loss program with excess up to a limit of 8.161 bn$ of which 30% is collateralized by various reinsurance companies. This is not much, considering it is estimated to value the exposure at over 500 bn$.
California Earthquake is probably the most traded risk in the reinsurance market worldwide. This is only a small company, there are over 12 m insured homes in the state of California, and only about 17 % of residencies are earthquake insured.
The CEA may buy a CAT XL program consisting of 525 m xs 250 m, 525 m xs 725 m and 600 m xs 1,300 m, and pay premiums of 320 k $, 179 k $ and 146 k $ respectively for each of the these layers at 10.4%, 7.85% and 3.65% Rol as an example. These ROL depend on the probability of an event of certain magnitude hitting the layer. It would be the mid-point of the layer. For example, a 10.4% ROL may mean a 12% probability of exhaustion of the layer xs 8% probability of activating the layer.
The volume of the aggregate exposure to a layer is given by physics of locations. Structures at different locations would be exposed to some events and some not, and to those exposed to some events will cause a damage and some not. In summary this determines the price of the layer.
It is important for modelling, Hazard U.S or HAZUS developed a loss estimation methodology together with the National Institute of building sciences. Modelling of earthquake risk considers building stock or specific location or site insured, local geology, size of potential earthquakes, economic data & other information to estimate potential cost from hypothetical earthquakes. Hence the cost of a financial or reinsurance instrument depends on the location and geophysics of the structures involved, and this data is therefore mandatory in most states.
However, much government education and preparedness has taken place over the past decades and building codes upgrades are incentivized in the policies. For example, the Hoover dam in Nevada was built to withstand horizontal ground acceleration of 0.1 g, correlating peak ground acceleration to a scale of earthquake intensity, like the Mercalli scale corresponds to Intensity of Mercalli VI with strong shaking, but light damage. There is a 2% chance in the next 50 years of an earthquake happening that could cause PGA (Peak Ground Acceleration) above engineering tolerances of the Hoover Dam in Nevada state.
The average residential California property portfolio comprises condominiums, single family dwelling, renters, and mobile homes.
Homeowner earthquake insurance covers home and structures attached to it, such as garage. Detached garages & pools are not covered. Typically, with 15% deductible, this has now been increased to 20 or 25% and up to 200,000 $ structural damage. Although there is also a buy-down policy deductible offered to lower the potential damage at an additional cost. Additional living expenses are also covered from standard 1,500 $ up to 100,000 $ limits, and contents from 5k $ up to 200k $. There are building codes upgrades & emergency repairs incentives.
Given NAIC, national association of insurance commissioner’s the annual average loss is around 6.14 bn $ per year. The 2016 state premium would be 73bn $ and Cat risk of 43 bn $.
Insurance companies operating in the state of California and taking residential earthquake risk are State Farm, Farmers with a 16% market share, CSAA, Allstate, Liberty Mutual, Nationwide, Travellers, the state CEA and Geovera among others.
There is also the California FAIR Plan which covers fire, or lightning, internal explosion & smoke. For additional premium, there is extended coverage for windstorm, hail, explosion, riot or civil commotion, aircraft, vehicles, and volcanic eruption coverage.
The FAIR plan pool does not cover all perils such as theft or liability, if so, there would be a requirement of additional ‘Difference in Conditions’ policies or DIC. Insurance companies offering this product are Catlin ins co, Nationwide, CSAA, Allstate, First American property & casualty, Kemper group, Liberty Mutual Group, Safeco ins co.
Premiums charges in California ranges from 3.7 $ (3.5 – 4) makes 2,960 $ / year for an 800,000 $ valued home. In San Andreas tectonic zone and over hundreds of smaller active faults earthquake risk is estimated at 75% change of a magnitude 7+ in the next 30 years or so.
In San Diego charges are 2.9 $ to 3.1 $ for 1000 $. A 575,000 $ family home would cost 1,725 $.
In San Francisco costs vary from 4 to 4.4 $ per 1,000 dollars of home structural value. It is estimated a 98% probability of an earthquake magnitude 6+ or greater in the Bay area in the next 30 years or so.
Insurance costs range from 0.6 to 15 $ per 1,000 value of coverage. Premium from 300 $ to $ 7,000 for 500,000 $ house.
Quotes be based on the number of stories and year built which in most states determines the building code as a minimum plus location and quality of structures.
The California department of Insurance was created in 1868, is the largest protection agency in the state of California, with an estimated 310 bn $ premiums.
Flood insurance is available from the government, earthquake insurance is not.
Damages caused by earthquake such as like fire, & water damage due to burst gas & water pipes provided by standard home & business insurance in most states.
Insurers not selling earthquake insurance may be still liable for damages caused by fire following earthquake, this be through either Business interruption policies or residential additional living expenses coverage.
Earthquake Exposure therefore in the state of California should include earthquake policies for EQ risk + FF EQ and non-earthquake policies for FF EQ. This is the case across the whole country and a challenge for catastrophe modelling. Fire Following EQ is two to three or more times bigger than the earthquake books and at times not modelled.
Residential Earthquake insurance has penetration rate of 17% in the West, 11% in the Midwest, 9% in the North East and 7% in the South. And deductibles are from 2-20% in Washington, Nevada & Utah with higher risks of EQ. Standard is 10% or a $ amount.
In most cases homeowners can get higher deductibles to save money on EQ premiums.
Exposure vulnerability and data quality assessment for a specialty book.
Wood frame buildings tend to withstand quake stresses better than other structures, like brick. In California 98% of residential property is wood frame for this reason, above sums insured quality for California Earthquake is for a specialty portfolio, e.g. mostly industrial facilities.
Pacific North West of the country costs are from 1-3 $ per 1,000 $ of coverage. In the East coast from 0.5 cents of a dollar per $ 1,000 limit.
Brick home in the Pacific North West cost from 3 – 15 $ and 0.6 to 0.9 cents in New York state.
1906 San Francisco earthquake caused movement of San Andreas fault and it is estimated to be 105 bn $ in 2020 economic and demographic conditions.
There is the issue of fracking or induced EQ which is proven to increase the frequency of earthquakes.
The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC), The U.S. Department of Energy & the electric power research institute published a study to reassess the vulnerability to earthquake in Central and Eastern U.S Nuclear power plants.



















Regional differences in rates are established by comparing expected losses from one ZIP code to another. Those who live in a ZIP code close to an earthquake fault or with predominantly poor soil can expect to pay more than those on firm soil, away from faults. Finally, using information the insured provides, the model accounts for the structure’s age and construction type. The resulting rate determines the premium for a CEA policy. Depending on its date of construction, a house that has been retrofitted may be entitled to a 5 percent premium discount. The CEA’s actuaries place ZIP codes that present similar seismic risk into “rating territories.”. This method of establishing rating territories produces rates that are more affordable for…